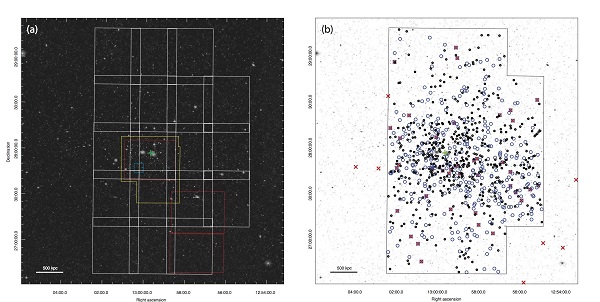
A team of space scientists from Stony Brook University and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan has revealed that about 854 dark galaxies were located within the Coma Hub, a discovery that became possible through using special telescope.
About 47 such dark galaxies were found last year, but discovering about 800 more has fascinated scientists because of the great importance that such discovery has to space science and astronomy.
While the researchers could not really tell where the galaxy nexus had been before this time or how it came into focus, they can only explain that it appeared to have been there all along but hidden by something they can’t really put their fingers on.
They state that while several of these galaxies could develop into a system the same size with those in our own Milky Way, some stars could be seen within the cluster. The only problem is that they are invisible from Earth because of something that blocks them from view and make them undetectable.
Jin Koda, principal investigator of the study and associate professor in the department of physics and astronomy at the university, stated that the galaxy must be covered by something massive, and that thing must be acting to protect the fragile stars within the galaxy from something unknown.
It is further believed that the invisible mass keeping the stars and galaxies from our view must be the historical dark matter, because this is known to make up about 99% of the galaxy cluster while real, hard matter make up only 1% of the cluster.
The researchers further discovered that many of the dark galaxies are no longer as bright as they used to be because they have now lost the gas that made them luminescent. However, while dark matter still generates controversy among space scientists like black holes, further research into the phenomenon continues.
Source: Stony Brook University.